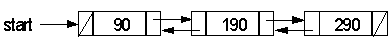
Sometimes it is useful to have a linked list with pointers to both the next and previous nodes. This is called a doubly linked list and may be declared as shown.
struct dblNode
{
int info;
dblNode* prev;
dblNode * next;
};
dblNode* start;

In this example, note that prev of the first node is set to NULL.
a. What are the advantages that this structure offers?
b. What are the disadvantages?
c. Compare doubly linked lists with singly linked lists. When would you choose to use one rather then the other?
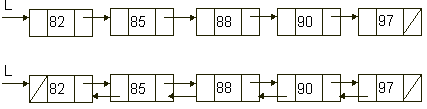
void MakeDL(dblNode* &L)
// pre-condition: L is singly-linked and possibly empty; see the first diagram
// post-condition: L is made doubly linked as shown above in the second diagram
{
void printForwardandBackward(dblNode* L)
// pre -condition: L is doubly linked and possibly empty
// post-condition: The integers stored in L are printed both forward and backward
// on two lines; for example, line 1: < 82 85 88 90 97 >
// line 2: < 97 90 88 85 82 >
{